This article originally appeared on Common Dreams on 3.3.21. You can read it here.
Emphasizing that the world still has a "fighting chance" to limit global warming with immediate and ambitious climate action, United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres on Tuesday urged governments and the private sector to cancel all planned coal projects, cease financing for coal-fired power plants, and opt instead to support a just transition by investing in renewable energy.
"Once upon a time, coal brought cheap electricity to entire regions and vital jobs to communities," Guterres said in a video message at the virtual meeting of the Powering Past Coal Alliance. "Those days are gone."
"Phasing out coal from the electricity sector is the single most important step to get in line with the 1.5 degree goal," Guterres continued, referring to the policy objective of preventing planetary temperatures from rising more than 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels. "Global coal use in electricity generation must fall by 80% below 2010 levels by 2030," he added.
According to Guterres, meeting the 1.5°C climate target this decade requires eliminating "the dirtiest, most polluting and, yes, more and more costly fossil fuel from our power sectors."
None— (@)
In his address, the U.N. chief outlined three steps that public authorities and companies must take to "end the deadly addiction to coal."
- Cancel all global coal projects in the pipeline;
- End the international financing of coal plants and shift investment to renewable energy projects; and
- Jump-start a global effort to finally organize a just transition.
Guterres called on the 37 members of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)—a group of relatively rich countries with a greater historical responsibility for extracting fossil fuels and emitting the greenhouse gasses that are causing deadly pollution and destroying the climate—to "commit to phasing out coal" by 2030, while urging non-OECD countries to do so by 2040.
Urging an end to global coal financing, Guterres called on all banks and investors to redirect their funds into the renewable energy sector. "All multilateral and public banks—as well as investors in commercial banks or pension funds—to shift their investments now in the new economy of renewable energy."
While stressing that "the transition from coal to renewable[s] will result in the net creation of millions of jobs by 2030," Guterres acknowledged that "the impact on regional and local levels will be varied."
"We have a collective and urgent responsibility to address the serious challenges that come with the speed and scale of the transition," he continued. "The needs of coal communities must be recognized, and concrete solutions must be provided at a very local level."
The U.N. chief urged "all countries to embrace the International Labor Organization's guidelines for a just transition and adopt them as minimum standard to ensure progress on decent work for all."
The coronavirus pandemic, Guterres noted, has "accelerated" the decline in "coal's economic viability," while recovery plans provide an opportunity to bring about a green transformation of the world's infrastructure.
In many parts of the world, a just transition dovetails with guaranteeing universal access to energy, said Damilola Ogunbiyi, CEO and special representative of the secretary-general for Sustainable Energy for All.
Ogunbiyi told conference attendees that almost 800 million people worldwide still lack access to basic electricity, while 2.8 billion are without clean cooking fuels.
"Right now, we're at a crossroads where people do want to recover better, but they are looking for the best opportunities to do that," she said. "And we're emphasizing investments in sustainable energy to spur economic development, create new jobs, and give opportunities to fulfill the full potential."
More on Good.is
California officials calmly shut down Trump's climate change denial ...
Whales can help climate change - GOOD
Climate change is unearthing artifacts from melting glaciers - GOOD















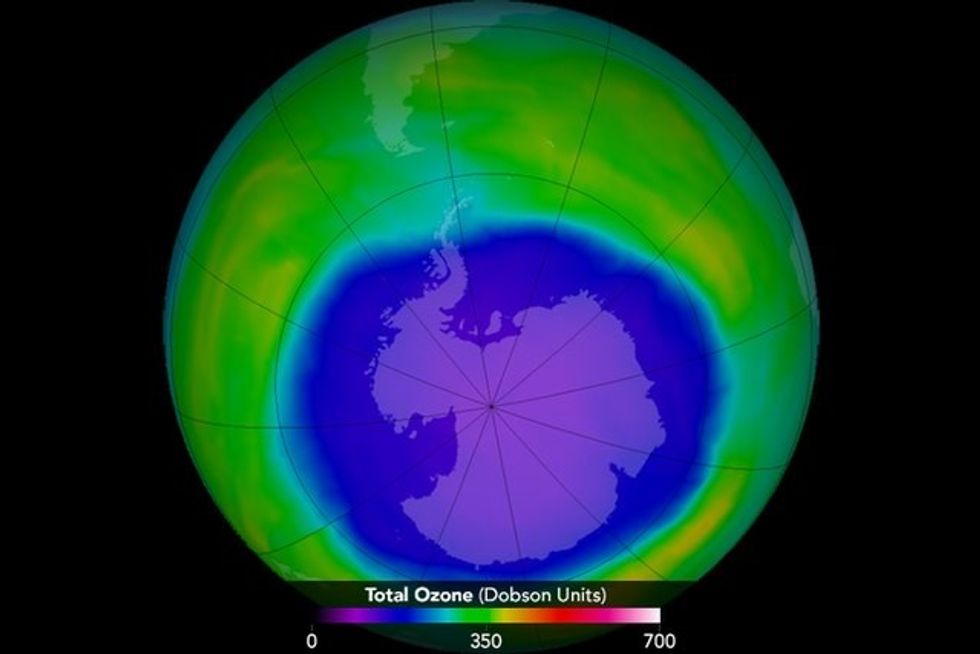 The hole in the ozone layer in 2015.Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons
The hole in the ozone layer in 2015.Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons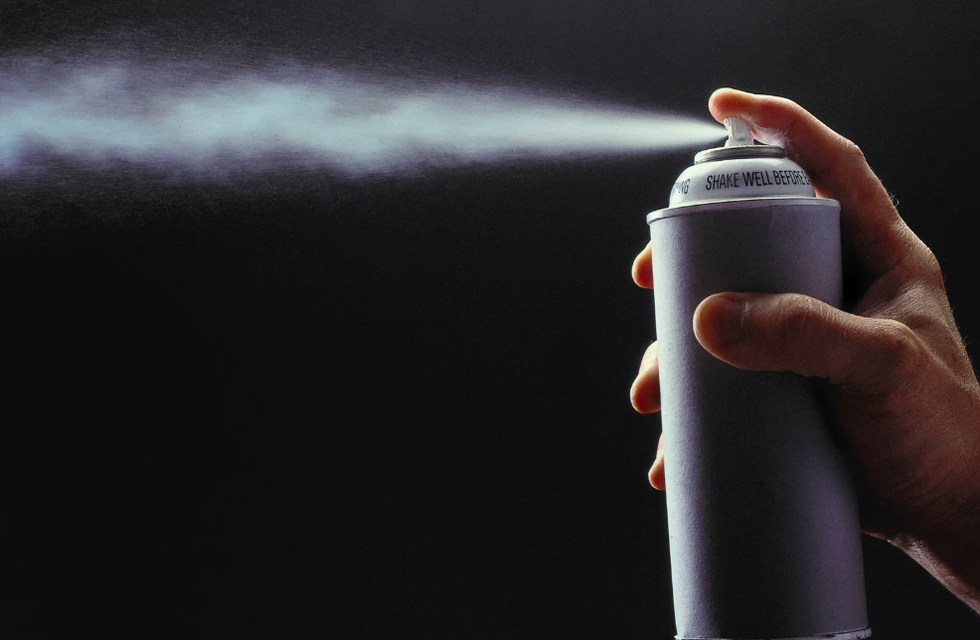 In the 1980s, CFCs found in products like aerosol spray cans were found to cause harm to our ozone layer.Photo credit: Canva
In the 1980s, CFCs found in products like aerosol spray cans were found to cause harm to our ozone layer.Photo credit: Canva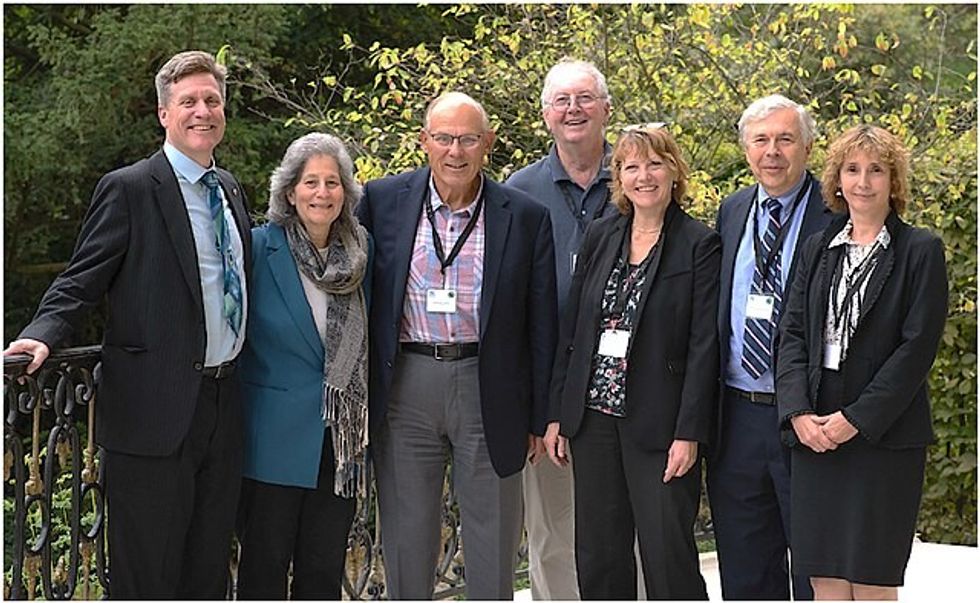 Group photo taken at the 30th Anniversary of the Montreal Protocol. From left to right: Paul Newman (NASA), Susan Solomon (MIT), Michael Kurylo (NASA), Richard Stolarski (John Hopkins University), Sophie Godin (CNRS/LATMOS), Guy Brasseur (MPI-M and NCAR), and Irina Petropavlovskikh (NOAA)Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons
Group photo taken at the 30th Anniversary of the Montreal Protocol. From left to right: Paul Newman (NASA), Susan Solomon (MIT), Michael Kurylo (NASA), Richard Stolarski (John Hopkins University), Sophie Godin (CNRS/LATMOS), Guy Brasseur (MPI-M and NCAR), and Irina Petropavlovskikh (NOAA)Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons
 Getting older means you're more comfortable being you.Photo credit: Canva
Getting older means you're more comfortable being you.Photo credit: Canva Older folks offer plenty to young professionals.Photo credit: Canva
Older folks offer plenty to young professionals.Photo credit: Canva Eff it, be happy.Photo credit: Canva
Eff it, be happy.Photo credit: Canva Got migraines? You might age out of them.Photo credit: Canva
Got migraines? You might age out of them.Photo credit: Canva Old age doesn't mean intimacy dies.Photo credit: Canva
Old age doesn't mean intimacy dies.Photo credit: Canva
 University President Eric Berton hopes to encourage additional climate research.Photo credit: LinkedIn
University President Eric Berton hopes to encourage additional climate research.Photo credit: LinkedIn
 Chewing helps blood flow to the brain.Photo credit: Canva
Chewing helps blood flow to the brain.Photo credit: Canva
 There are many applications for 3D printing to explore.Photo credit: Canva
There are many applications for 3D printing to explore.Photo credit: Canva


















 The types of tea, tea bags, and seeping time impact how much metal can be removed from water.Photo credit: Canva
The types of tea, tea bags, and seeping time impact how much metal can be removed from water.Photo credit: Canva Water filtration is still a need throughout the world.Photo credit: Canva
Water filtration is still a need throughout the world.Photo credit: Canva Tea drinking is a staple in many different cultures throughout the world.Photo credit: Canva
Tea drinking is a staple in many different cultures throughout the world.Photo credit: Canva