You might not have quite the same zeal for candy consumption as an adult that you did back when you were eight or nine years old, but chances are you’re not going to completely abstain this Halloween. However, if you’re really planning on tying one on this holiday, it might be helpful to know how much your body can physically take before throwing in the towel.
Fortunately, the folks over at the science-focused YouTube channel Reactions have put together a handy video guide that lets us know when to say when before consuming too much candy causes us to, uh, die. It also does a great job of explaining what excess sugar consumption does to our bodies that can be so dangerous.
Chances are adults or kids with even the biggest sweet tooth will stop well short of the 1,627 pieces of candy corn necessary to do them in, but…you never know. These things always have a way of getting away from you, don’t they? Considering those little devils are almost straight sugar, they pack far more of a wallop on your liver (usually the weak link when it comes to sugar toxicity) than chocolate snacks do.
That said, if candy corn isn’t your cup of tea, or you’re not really looking to take down more than a thousand of them, the guide also gives us the equivalent in “fun size” candy bars. In the event that you grossly overestimated the trick-or-treater foot traffic in your neighborhood, you could partake in 262 leftover pieces before shuffling the mortal coil.
These numbers sound stratospheric, sure, but bear in mind that consumption of sugar can actually make you hungrier. So to some extent, the more candy you eat, the more candy you’ll want to eat. But practically, all sorts of digestive and chewing mechanisms might go kaput before you reach the thresholds in the guide.
You’re probably not going hit these crazy-high figures in the course of an evening, but habitually high consumption of sugar can have consequences that are equally dangerous, if less dramatic.
Check out the longer-term (and more likely) effects of excess sugar consumption in this video on sugar toxicity:















 Freddie Mercury GIF by Queen
Freddie Mercury GIF by Queen File:Statue of Freddie Mercury in Montreux 2005-07-15.jpg - Wikipedia
File:Statue of Freddie Mercury in Montreux 2005-07-15.jpg - Wikipedia
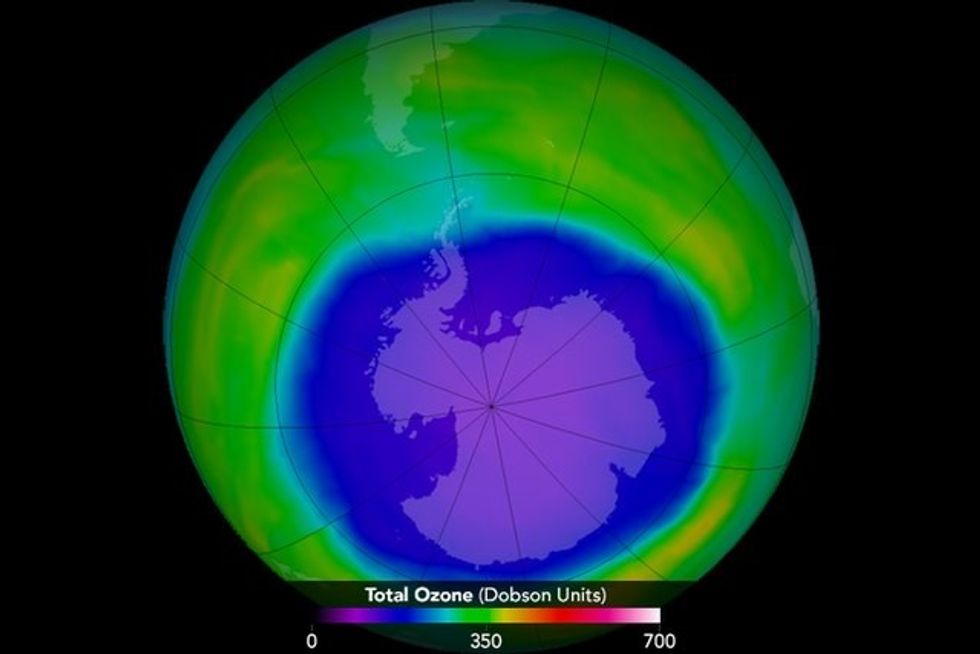 The hole in the ozone layer in 2015.Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons
The hole in the ozone layer in 2015.Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons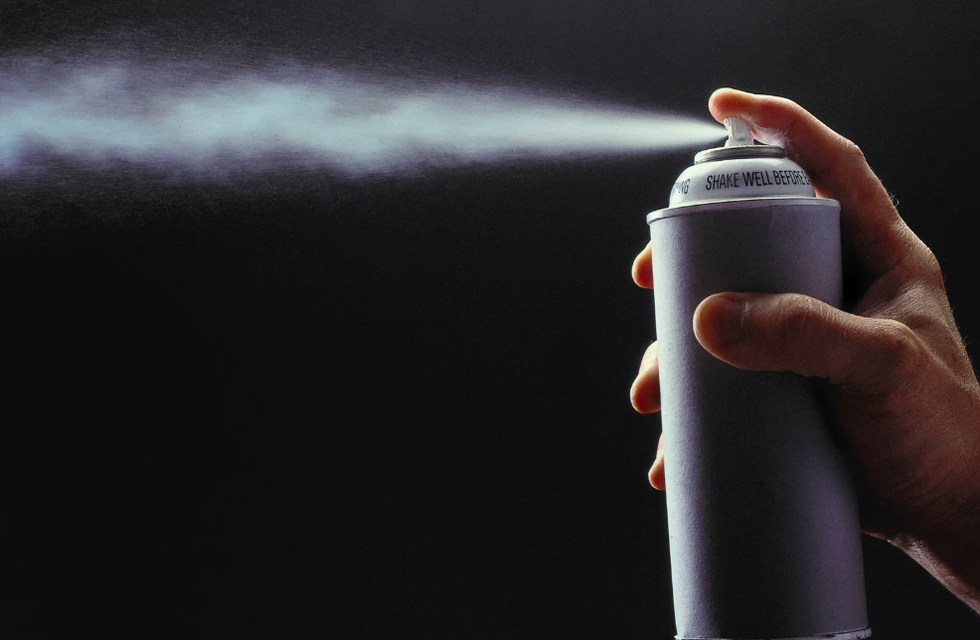 In the 1980s, CFCs found in products like aerosol spray cans were found to cause harm to our ozone layer.Photo credit: Canva
In the 1980s, CFCs found in products like aerosol spray cans were found to cause harm to our ozone layer.Photo credit: Canva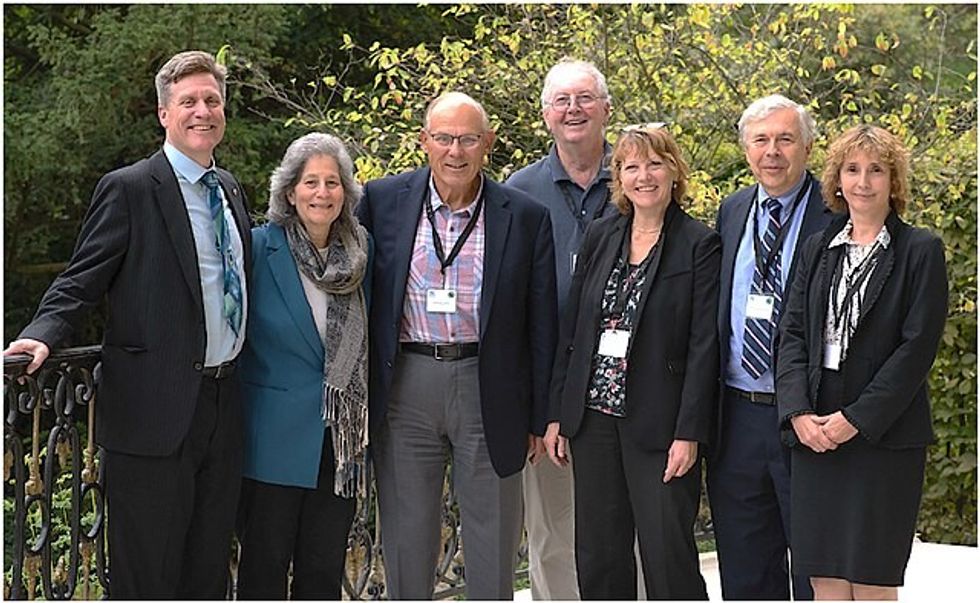 Group photo taken at the 30th Anniversary of the Montreal Protocol. From left to right: Paul Newman (NASA), Susan Solomon (MIT), Michael Kurylo (NASA), Richard Stolarski (John Hopkins University), Sophie Godin (CNRS/LATMOS), Guy Brasseur (MPI-M and NCAR), and Irina Petropavlovskikh (NOAA)Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons
Group photo taken at the 30th Anniversary of the Montreal Protocol. From left to right: Paul Newman (NASA), Susan Solomon (MIT), Michael Kurylo (NASA), Richard Stolarski (John Hopkins University), Sophie Godin (CNRS/LATMOS), Guy Brasseur (MPI-M and NCAR), and Irina Petropavlovskikh (NOAA)Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons
 Getting older means you're more comfortable being you.Photo credit: Canva
Getting older means you're more comfortable being you.Photo credit: Canva Older folks offer plenty to young professionals.Photo credit: Canva
Older folks offer plenty to young professionals.Photo credit: Canva Eff it, be happy.Photo credit: Canva
Eff it, be happy.Photo credit: Canva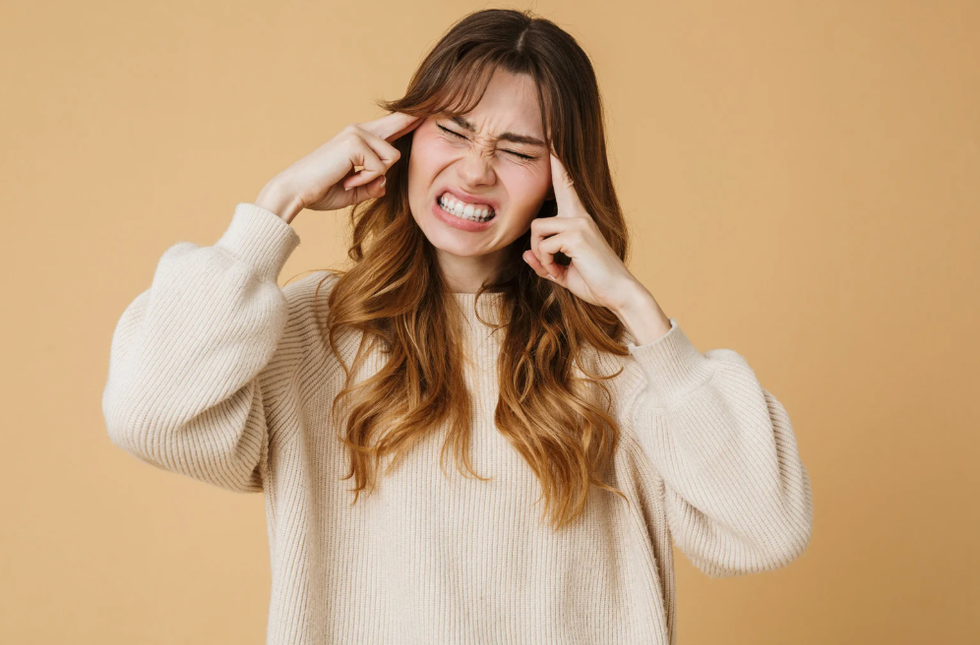 Got migraines? You might age out of them.Photo credit: Canva
Got migraines? You might age out of them.Photo credit: Canva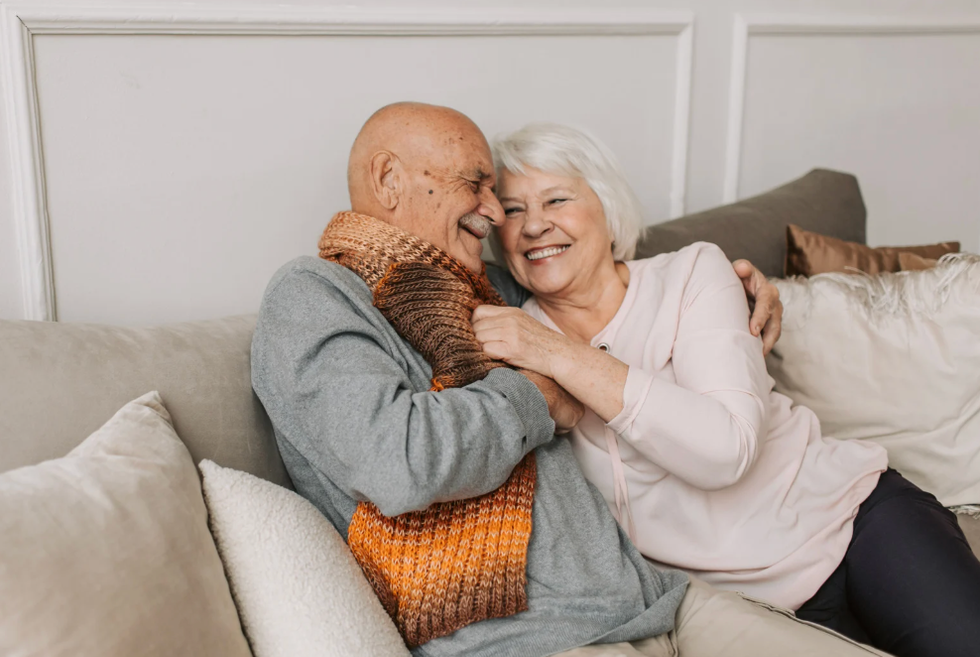 Old age doesn't mean intimacy dies.Photo credit: Canva
Old age doesn't mean intimacy dies.Photo credit: Canva
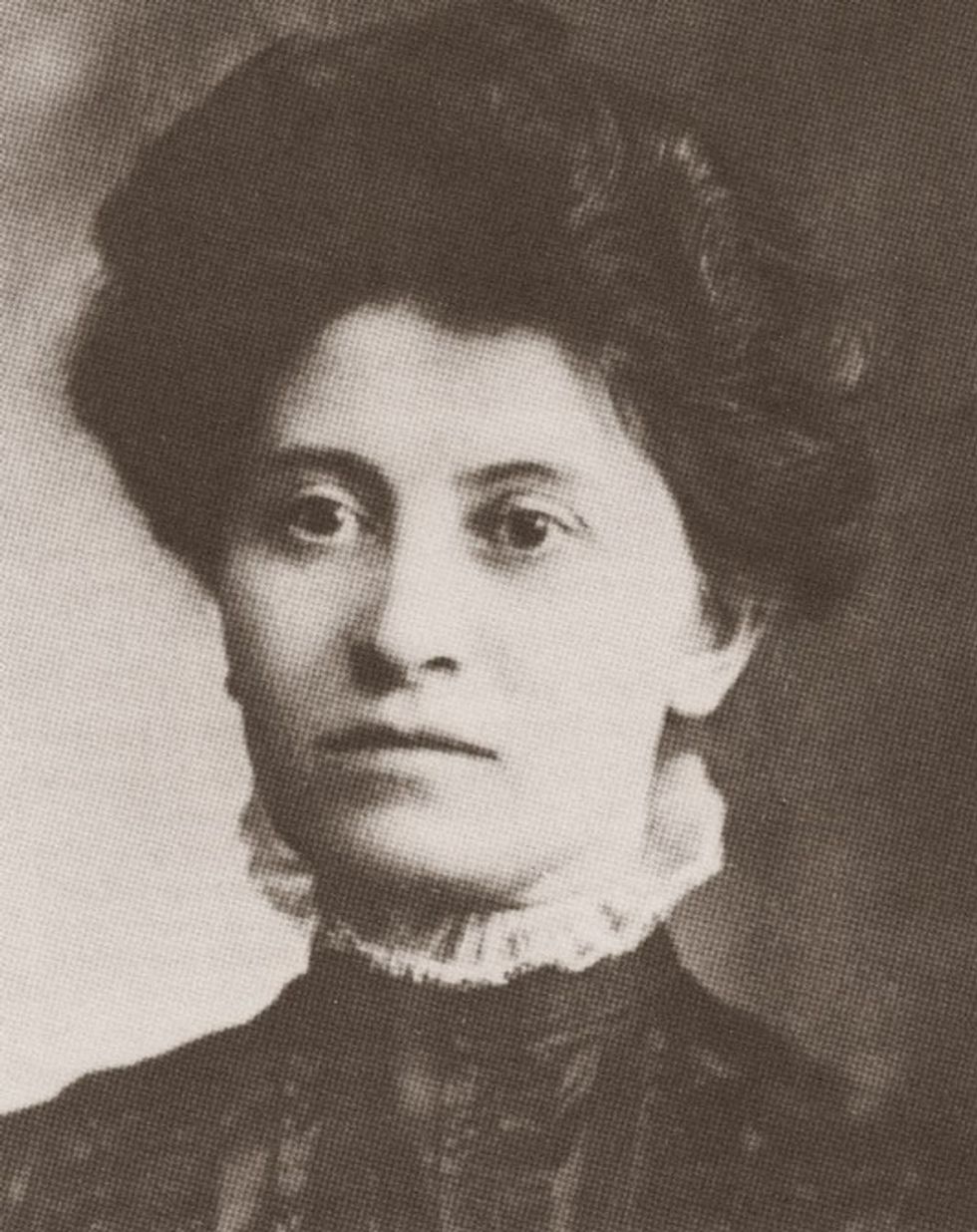 Theresa Malkiel
commons.wikimedia.org
Theresa Malkiel
commons.wikimedia.org
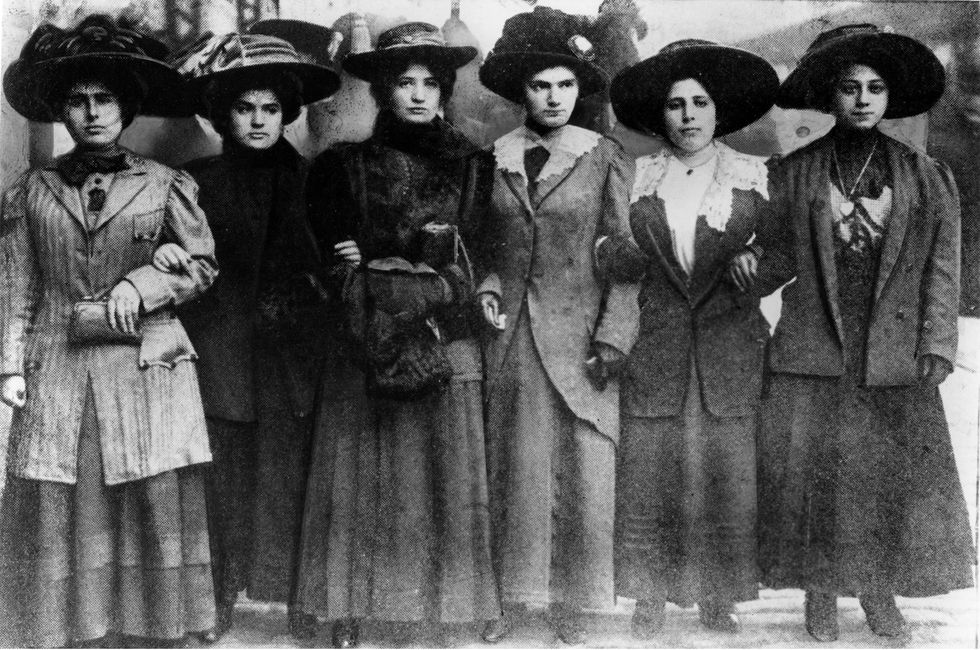 Six Shirtwaist Strike women in 1909
Six Shirtwaist Strike women in 1909
 University President Eric Berton hopes to encourage additional climate research.Photo credit: LinkedIn
University President Eric Berton hopes to encourage additional climate research.Photo credit: LinkedIn
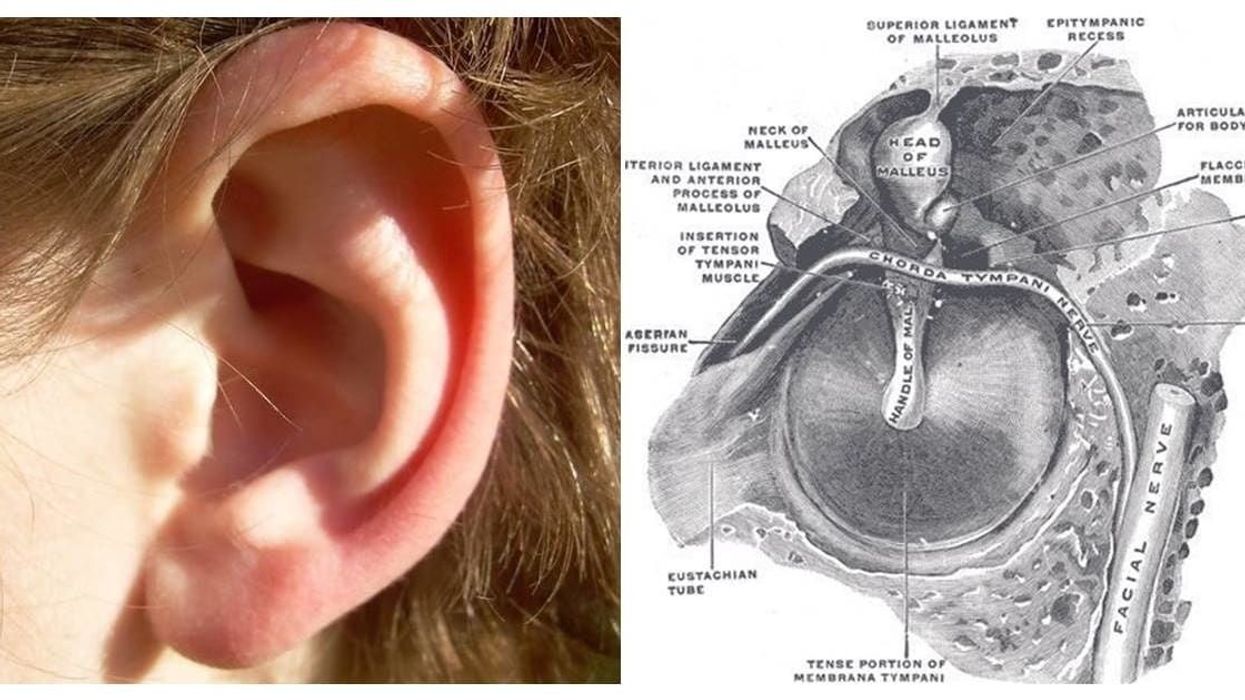
 Image by Ildar Sajdejev via GNU Free License | Know your rights.
Image by Ildar Sajdejev via GNU Free License | Know your rights.