The moon is one of the universe's most dazzling spectacles, but medieval lore suggests it also held mystical powers. In European mythology, people believed that a full moon could transform humans into werewolves. Even Greek philosopher Aristotle and Roman historian Pliny the Elder suggested the moon could negatively influence the human brain. However, one American mathematician took things further, proposing that destroying the moon could solve all of humanity's problems. His eccentric theory, recently resurfaced from People's 1991 archives, is now the subject of much academic humor.

Alexander Abian was a mathematics professor at Iowa State University. In a 1991 campus newsletter, he proposed his “Moonless Earth theory,” according to which “blowing up the Moon would solve all of human life’s problems.” He didn’t have a personal grudge for the moon, but rather he believed that demolishing it would mean the end of seasons, which would eliminate natural disasters.
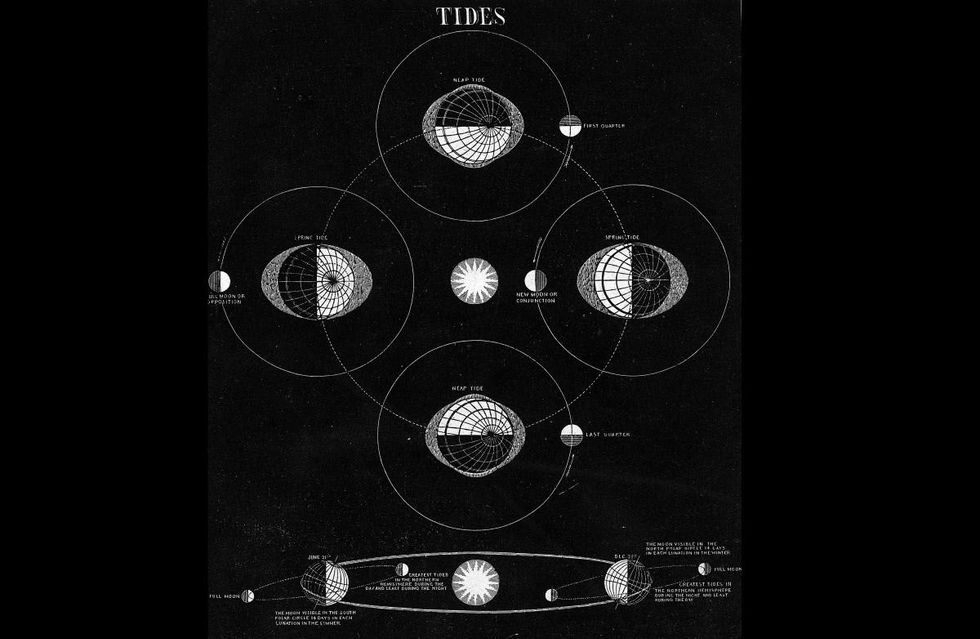
Abian’s hypothesis was based on the idea that if the moon no longer existed, Earth’s rotation would stop, and this would change the temperatures and wind patterns for good. He said “nuking the moon” was the idea, and the means to do this was nuclear force. “You make a big hole by deep drilling, and you put there atomic explosive, and you detonate it—by remote control from Earth.”
Sounds pretty convenient, but it isn’t. Over the years, scientific experts and astronomers have expressed strong disapproval and criticism of this idea. Many have even said that a moonless Earth would lead to a total collapse of life on the planet. For instance, speaking to Popular Mechanics, Katiya Fosdick of MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research said that destroying the moon would not eliminate natural disasters, but cause exactly the opposite, “I think that would create natural disasters.”

Abian may have been right that destroying the moon would make tides smaller, but they wouldn’t disappear entirely, as the Sun also affects tides. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), tides are “very long-period waves that move through the ocean in response to the forces exerted by the moon and sun.” As they rise and fall, tides influence ocean currents, determining whether the weather is cool or hot.
If the moon were to disappear and tides lessened, the weather might seem more stable, but it would trigger other serious issues. Tides are responsible for maintaining the ecological balance. No tides would mean disorder in biological life. Food chains will be affected, and so will be cosmological timekeeping. Earth’s rotation will gradually slow down and it will start freezing. “Think about half the Earth not receiving any sunlight for two-thirds of the year,” said Fosdick.

Plus, there are various science-based reasons why Earth “needs” the Moon to be there. Life on Earth can’t possibly survive without its only natural satellite, as BBC’s Science Focus also explains. There are three major explanations. First is the intensity of nuclear energy that would be required to blast away the Moon to smithereens. Mankind would need to drill mine shafts hundreds of kilometers deep, all over the Moon, and drop a total of 600 billion of the largest nuclear bombs ever built down them.

Added to it, is the fiery rain of debris that the blasted Moon will shower on the Earth. Even a small pebble-sized fragment falling on the planet from the Moon would be lethal to humans. The fragments would burn, releasing enormous quantities of kinetic energy into the atmosphere, heating it until all life was incinerated. Just one collision could spur a chain reaction of crashes, filling Earth’s orbit with so much space debris that it would choke up the planet’s life. This phenomenon is also referred to as “Kessler Syndrome,” proposed by NASA scientist Donald J. Kessler in 1978 and also seen in Neal Stephenson's 2015 novel "Seveneves."
A moonless Earth would prompt another life-destroying scenario by affecting the “tilt” of the planet. The debris from the Moon will scatter and stick to the rings around the planet. Over the years, the Earth’s axial tilt would become so disharmonized that most of one hemisphere would face the Sun continuously, and the other would be in perpetual darkness.
Yet, Abian’s belief in the moonless theory remained unshakeable till the end of his life. When challenged, he said, “I am raising the petulant finger of defiance to the solar organization for the first time in 5 billion years. Those critics who say ‘Dismiss Abian’s ideas’ are very close to those who dismissed Galileo.”



















 Music isn't just good for social bonding.Photo credit: Canva
Music isn't just good for social bonding.Photo credit: Canva Our genes may influence our love of music more than we realize.Photo credit: Canva
Our genes may influence our love of music more than we realize.Photo credit: Canva
 Great White Sharks GIF by Shark Week
Great White Sharks GIF by Shark Week

 Blue Ghost Mission 1 - Sunset Panorama GlowPhoto credit:
Blue Ghost Mission 1 - Sunset Panorama GlowPhoto credit: 
 medical school brain GIF
medical school brain GIF woman leaning on man's shoulder
Photo by
woman leaning on man's shoulder
Photo by 
 Ripe bananas
Ripe bananas How we treat produce could be changing for the better.
How we treat produce could be changing for the better.