Search
Latest Stories
Start your day right!
Get latest updates and insights delivered to your inbox.
We have a small favor to ask of you
Facebook is critical to our success and we could use your help. It will only take a few clicks on your device. But it would mean the world to us.

Here’s the link . Once there, hit the Follow button. Hit the Follow button again and choose Favorites. That’s it!
The Latest
Most Popular
Sign Up for
The Daily GOOD!
Get our free newsletter delivered to your inbox
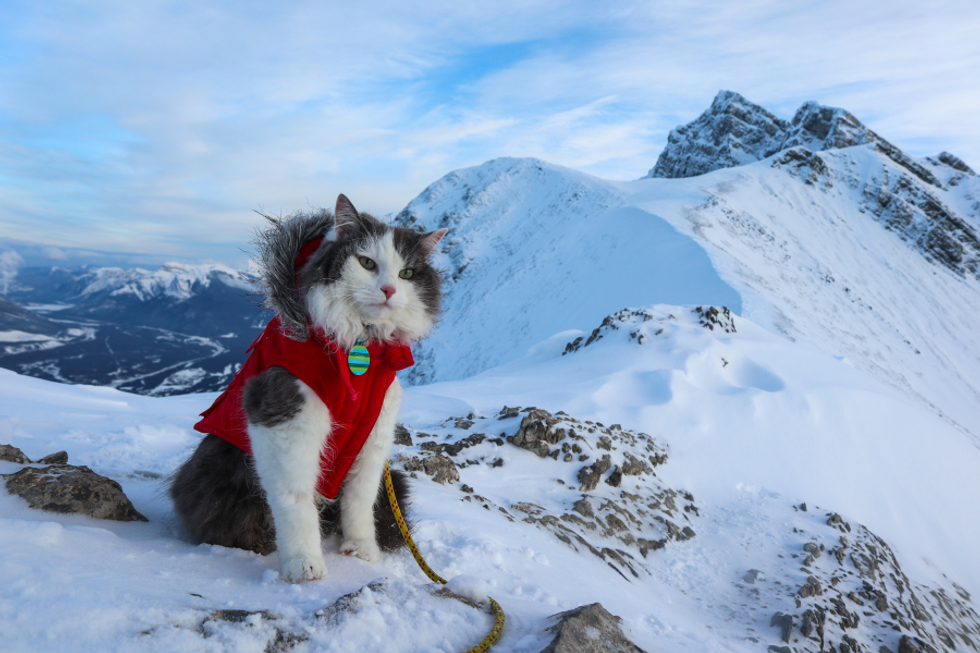












 Let us all bow before Gary, the Internet's most adventurous feline. Photo credit: James Eastham
Let us all bow before Gary, the Internet's most adventurous feline. Photo credit: James Eastham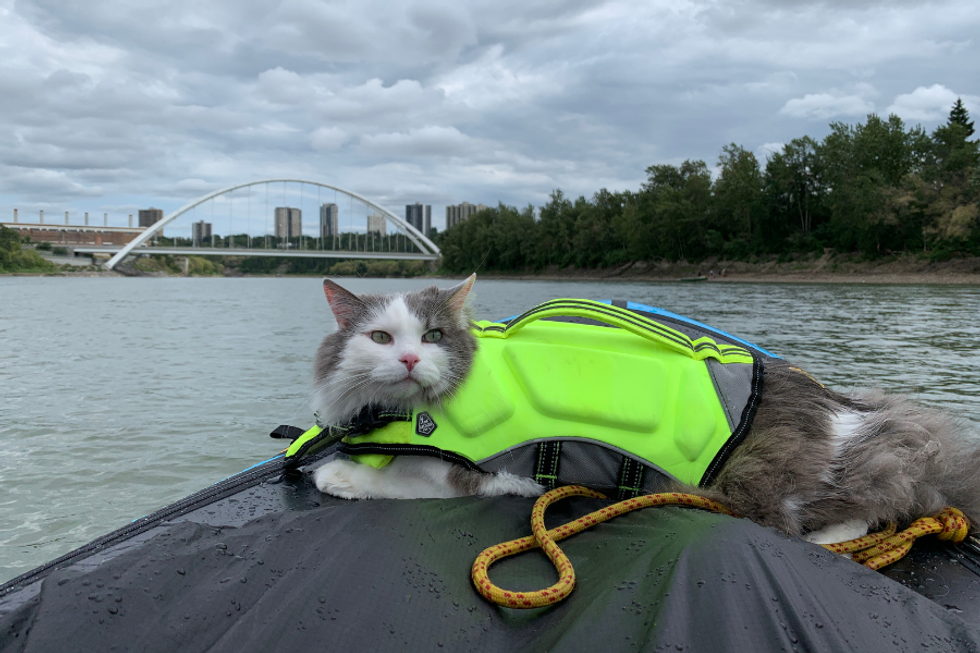 Gary the Cat enjoys some paddling. Photo credit: James Eastham
Gary the Cat enjoys some paddling. Photo credit: James Eastham James and Gary chat with Ryan Reed and Tony Photo credit: Ryan Reed
James and Gary chat with Ryan Reed and Tony Photo credit: Ryan Reed
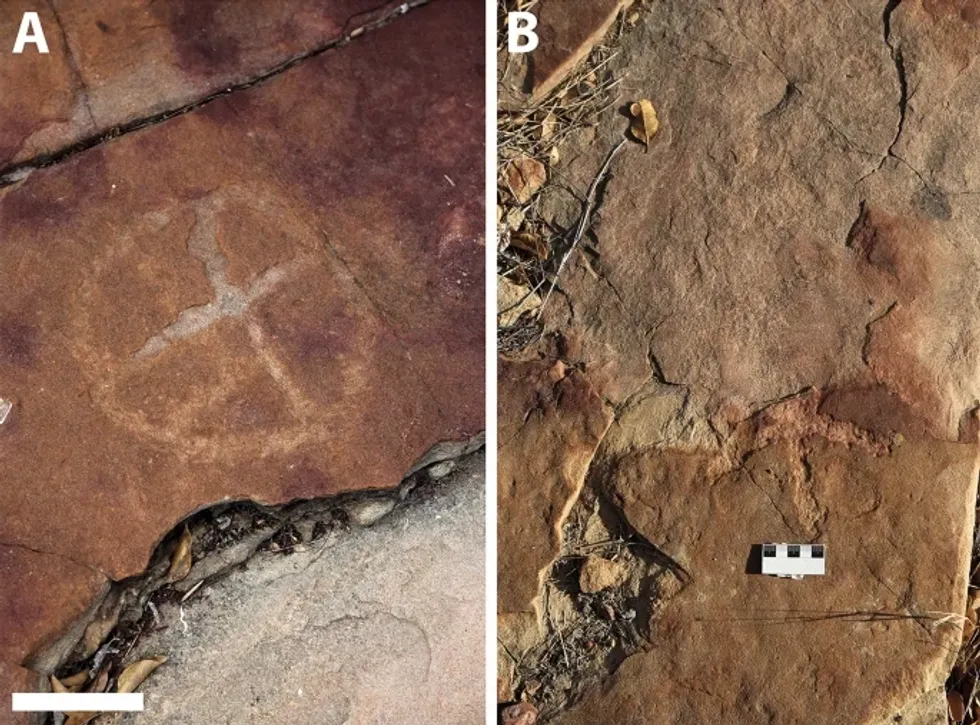

 Rock deterioration has damaged some of the inscriptions, but they remain visible. Renan Rodrigues Chandu and Pedro Arcanjo José Feitosa, and the Casa Grande boys
Rock deterioration has damaged some of the inscriptions, but they remain visible. Renan Rodrigues Chandu and Pedro Arcanjo José Feitosa, and the Casa Grande boys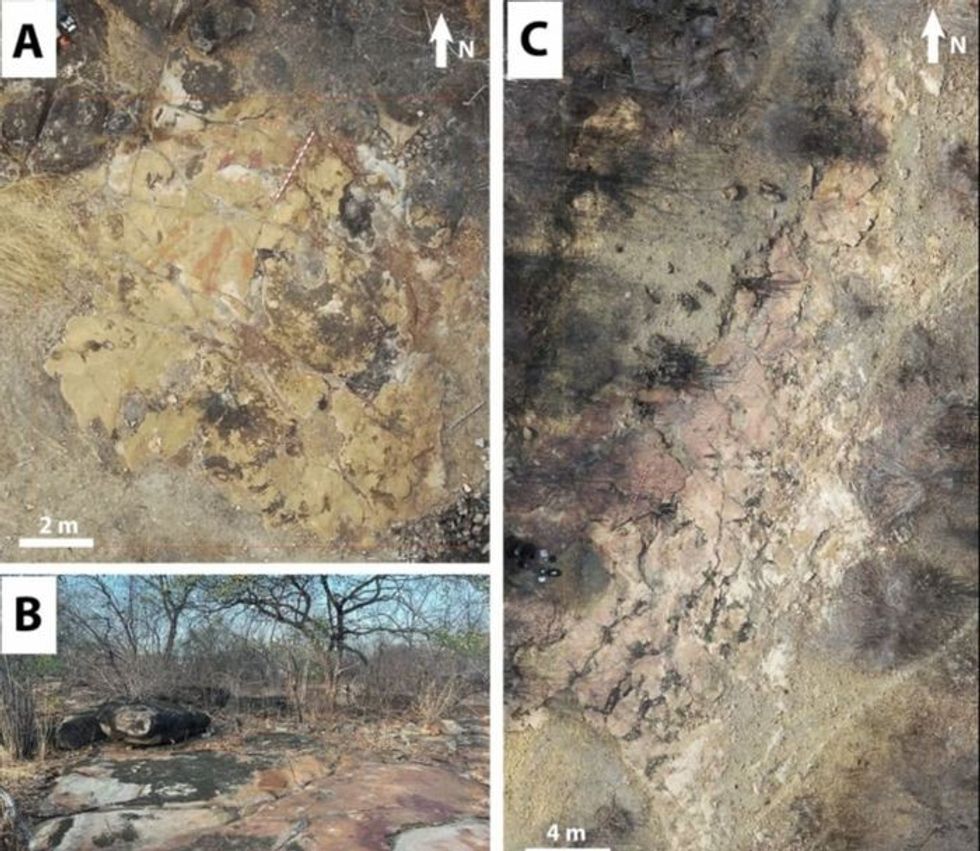 The Serrote do Letreiro site continues to provide rich insights into ancient life.
The Serrote do Letreiro site continues to provide rich insights into ancient life.
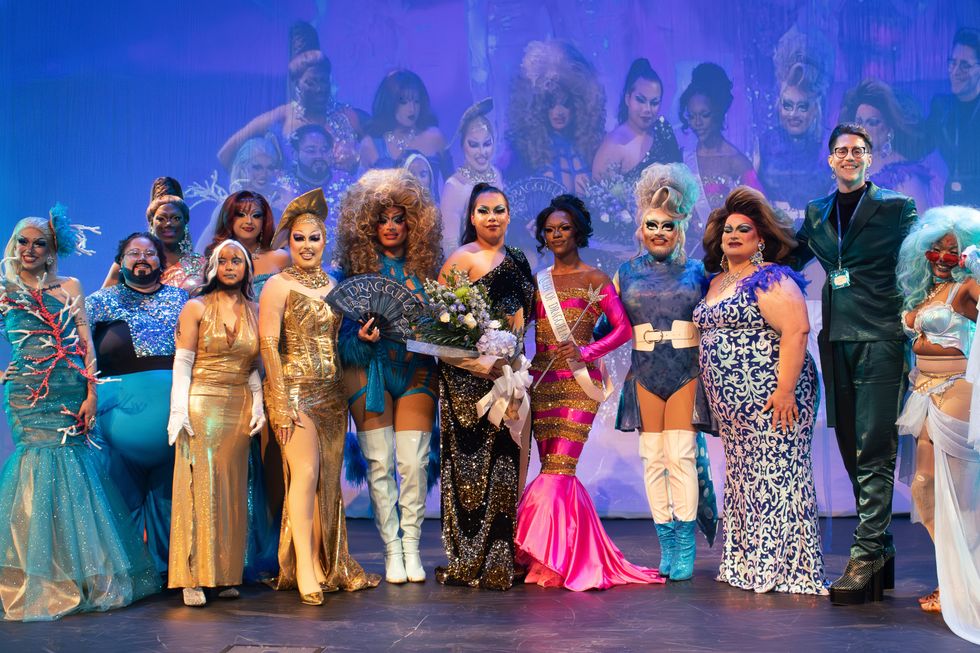
 The contestants and hosts of Draggieland 2025Faith Cooper
The contestants and hosts of Draggieland 2025Faith Cooper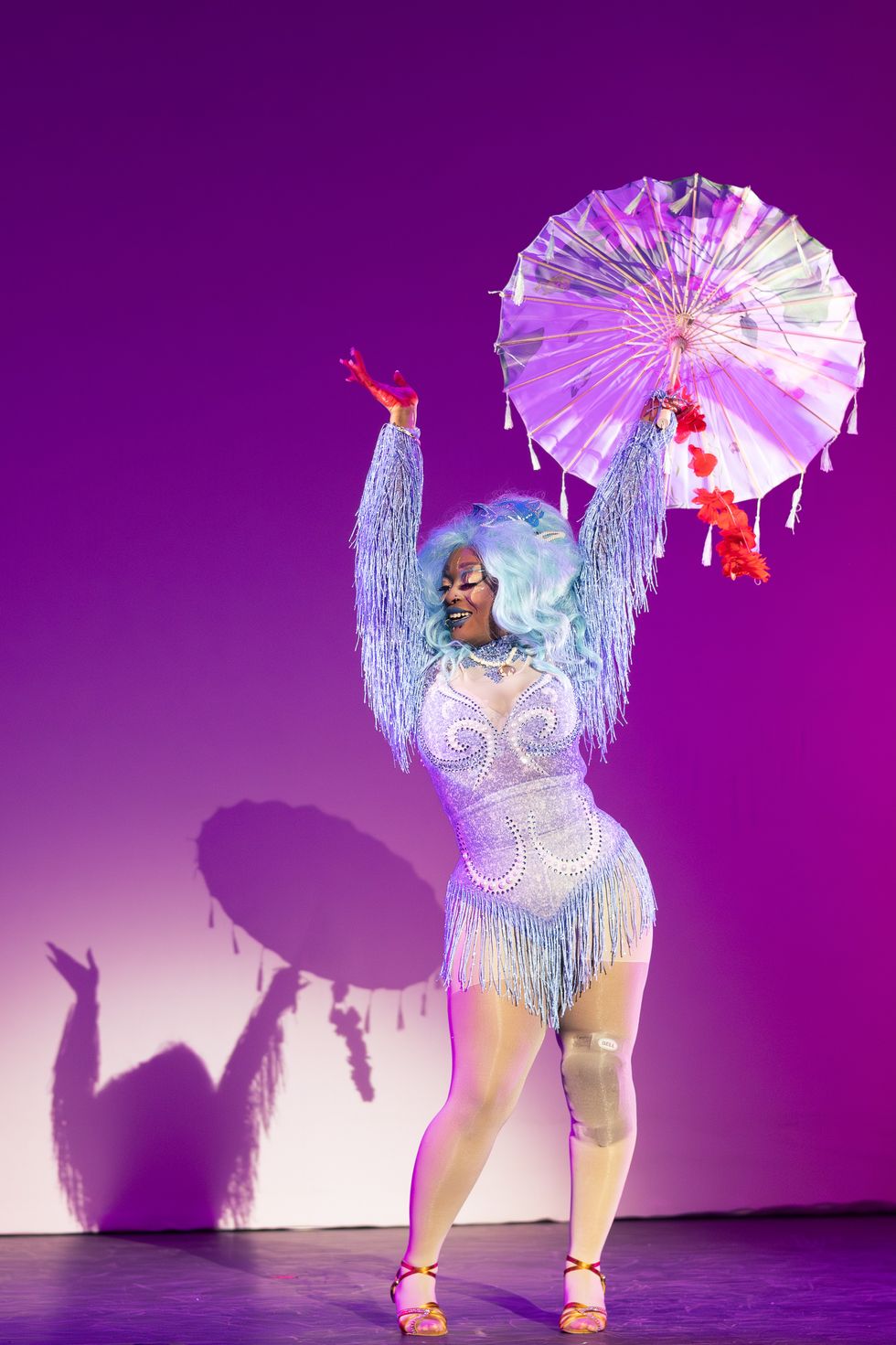 Dulce Gabbana performs at Draggieland 2025.Faith Cooper
Dulce Gabbana performs at Draggieland 2025.Faith Cooper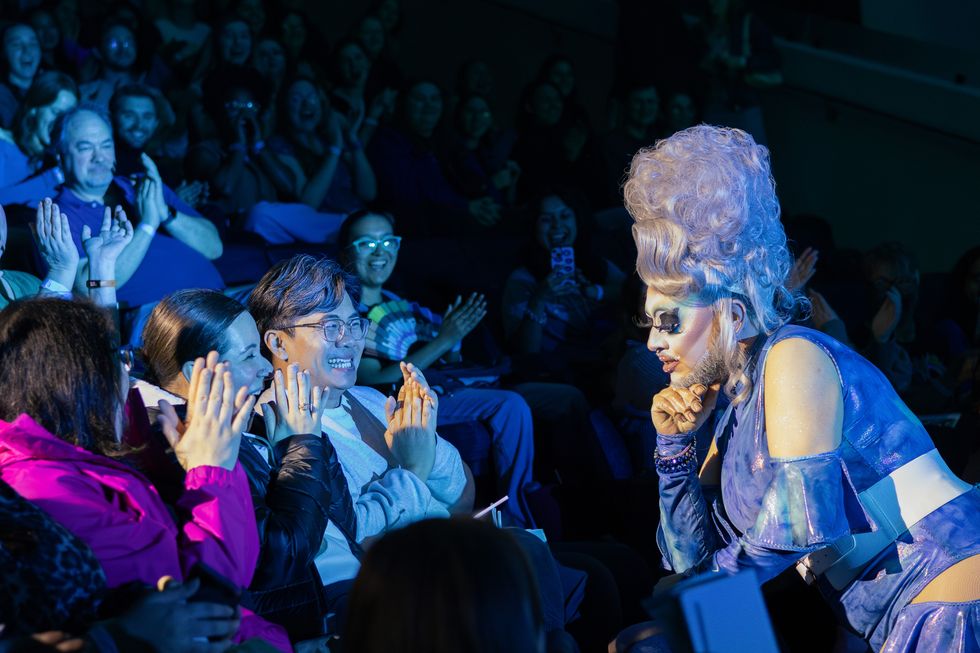 Melaka Mystika, guest host of Texas A&M's Draggieland, entertains the crowd
Faith Cooper
Melaka Mystika, guest host of Texas A&M's Draggieland, entertains the crowd
Faith Cooper


